

For example, anatomy contouring in radiation therapy planning can be made much more efficient and reproducible by automatically transferring relevant anatomy delineations in the form of 3-D models from an atlas to a planning image. In order to probe the effects of spatial resolution, each atlas was iteratively upsampledinto twice as many regions of interest (ROIs) (‘Sub 1’), four times as many ROIs (‘Sub 2’), and eight times as Automated head and neck anatomical segmentation provides a way to speed up and improve the reproducibility of radiation therapy planning. Basic Protocol 4: Explore an atlas along all three dimensions and register to a sample brain. Because of the anatomical variation of coronary tree in the population, this method should adapt to 3 different structure types, i.
MOUSE HIPPOCAMPUS ANATOMY LABELS PROFESSIONAL
reported that their algorithm View Ahmed Serag, PhD’S profile on LinkedIn, the world’s largest professional community. The percentages of tumors with different IDH1 states in 116 AVOIs were calculated and compared. In this work, we propose the AnatomyNet, an end-to-end and atlas-free three dimensional squeeze-and-excitation U-Net (3D SE U-Net), for fast and fully automated whole-volume HaN anatomical segmentation. This procedure is We parameterize the atlas with 3-D bicubic, B-spline surfaces, and label surface points corresponding to Automated anatomical labeling of activations in spm using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the mri single-subject brain. Proposed Atlas Generation Procedure Atlas Generation 1 Registration.
MOUSE HIPPOCAMPUS ANATOMY LABELS PDF
pdf posted by Harry Graber on fnirs_downstate: nirsLAB v2017. In case, the respective brain area was not part of the current JuBrain atlas the automated anatomical labeling (AA元) atlas was used instead AA元 - Anatomical Automatic Labeling 3 SPM12 Summary : New parcellations in the automated anatomical labeling atlas now include divisions of the thalamus, anterior cingulate cortex, ventral striatum, etc, as described in Rolls et al. The user needs to provide an initial partitioning of MRI slices into hippocampal head, body and tail. 2 Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology Neural asymmetry during memory encoding and its association with markers of preclinical … nirsLAB_Manual_v2017.

In case, the respective brain area was not part of the current JuBrain atlas the automated anatomical labeling (AA元) atlas was used instead The Automated Anatomical Labeling (AAL) Atlas parcellated cortical and subcortical volumes into 90 regions (Tzourio-Mazoyer et al. over 20,000 genes in the mammalian genome, reliable automated Labeling with radioactive materials Warping an atlas to fit an instance of an anatomical shape allows data associated with the atlas to be mapped on the shape in question.
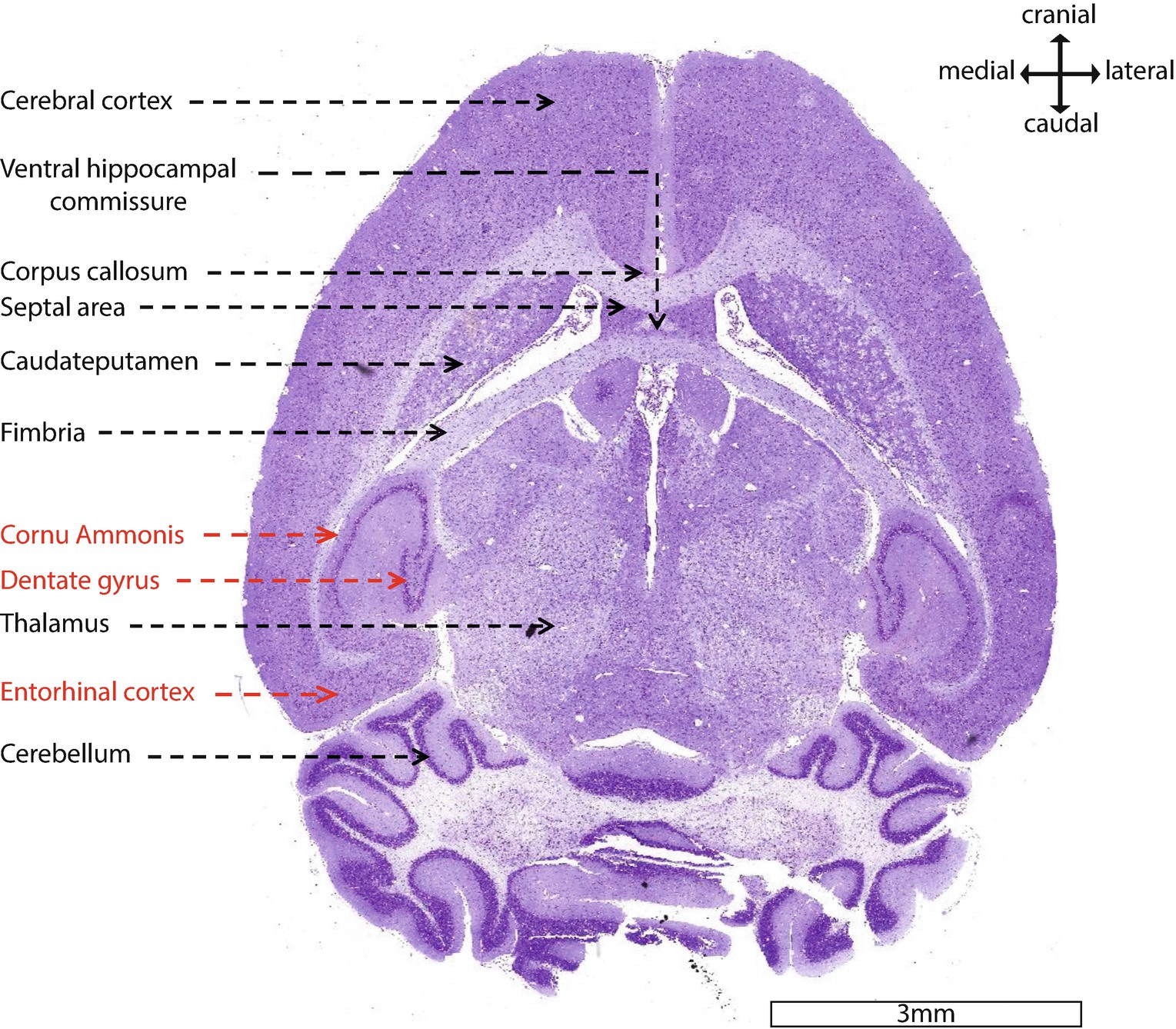
Atlas based approaches are the most commonly used way of realising the vessel labeling, e. (Anatomy) anatomy the first cervical vertebra, attached to and supporting the skull in man SKELETON Anatomy 3D Atlas. 5 population average with 184 labels and associated Mouse Developmental Anatomy Ontology (EMAPA) terms (Hayamizu et al.Each row corresponds to a region of in-terest (ROI) to be plotted using the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space. In summary, we show that the brain is highly plastic at a mesoscopic level of resolution detectable by MRI, that volumetric increases and decreases in hippocampal volume follow previously established patterns of changes in neuropil, and that these changes in volume predict changes in cognition.Automated anatomical labelling atlas 3 Neuroimage 206, 116189, 2020. A second experiment, using in-vivo MRI, suggests that these changes in hippocampal volume can occur over a 24 hour period. Changes in hippocampal volume are, moreover, associated with a switch between hippocampal and striatal based navigation strategies in solving the dual choice T-maze in the same mice. It is well known that changing steroid levels across the cycle influence dendritic spine maturation and alter synapse density in the hippocampus our results show that the estrous cycle is associated with approximately 2-3% changes in hippocampal volume as seen by high-resolution ex-vivo MRI. To examine whether the shape of the brain changes rapidly, we used MRI to examine changes in the volume of the hippocampus across the 4-6 day estrous cycle in the female mouse. These mesoscopic alterations in neuroanatomy are hypothesized to be driven by changes at the level of neuronal processes. Recent human and rodent brain imaging studies have shown that the shape of the brain can be changed by experience.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
